Testosterone replacement therapy has gained traction among men hoping to tackle symptoms of low testosterone. Still, figuring out when and how to use it isn’t as straightforward as it might seem. Doctors only recommend testosterone replacement therapy if both symptoms and lab tests point to a real hormone deficiency, so getting an accurate diagnosis matters a lot before jumping in.
Let’s get into what really matters about testosterone therapy. We’ll look at how to spot genuine deficiency symptoms, and what treatment options are actually out there.
The decision to start hormone replacement isn’t simple. You’ve got to weigh the possible benefits against some real risks and side effects.
Understanding Testosterone Replacement Therapy
Testosterone replacement therapy steps in when your body can’t make enough of this hormone on its own. It’s a medical treatment that involves different ways of getting testosterone back up to healthy levels.
What Is Testosterone Replacement Therapy?
TRT, or testosterone replacement therapy, means supplementing or replacing testosterone if your body just isn’t making enough. Doctors use TRT to get testosterone levels back up to what’s considered a normal range.
TRT comes in several forms:
- Injections (weekly or bi-weekly)
- Topical gels you rub on daily
- Patches you stick on your body
- Pellets implanted under the skin
- Nasal gels
The goal is to bring testosterone somewhere between 300-1000 ng/dL. Doctors keep a close eye on your blood levels to make sure you’re getting the right dose.
Most guys get injections of testosterone cypionate or enanthate. These long-acting shots help keep things steady.
How Testosterone Functions in the Body
Testosterone is the main male sex hormone, and honestly, it has its hands in a lot of stuff. The testes do most of the work making testosterone, though the adrenal glands chip in a tiny bit too.
Key functions of testosterone include:
- Sexual development: Drives penis and testicle growth at puberty
- Muscle mass: Keeps muscles strong and healthy
- Bone density: Maintains bone strength and helps prevent breaks
- Red blood cell production: Boosts blood oxygen levels
- Mood regulation: Affects energy and mental outlook
The brain controls testosterone production using the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. They send out signals that tell the testes to get to work.
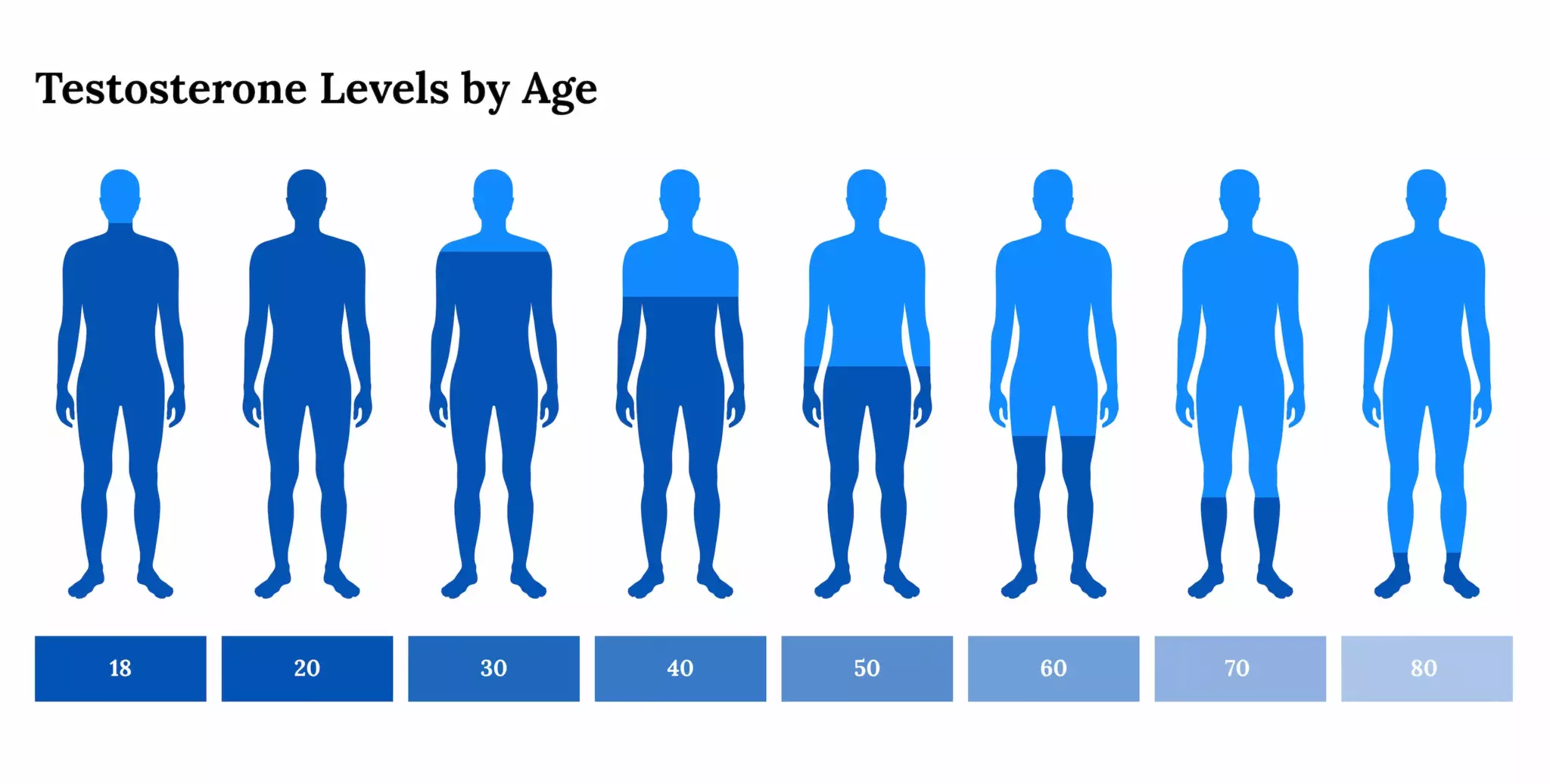
Testosterone levels naturally dip as you age—about 1-2% per year after 30. Most older men still stay in the normal range, but some see a real drop-off.
Causes of Low Testosterone and Hypogonadism
Low testosterone, or hypogonadism, means your body can’t make enough hormone to keep things running smoothly. Doctors usually divide it into two types, depending on where the problem starts.
Primary hypogonadism hits the testes directly:
- Testicular injury from trauma or infection
- Genetic issues like Klinefelter syndrome
- Cancer treatments, especially chemo
- Undescended testicles at birth
Secondary hypogonadism starts with the brain’s hormone signals:
- Pituitary gland problems or tumors
- Head injuries that mess with hormone centers
- Chronic illnesses (think diabetes, kidney disease)
- Certain meds, especially opioids
Age is the main culprit for testosterone decline, but lifestyle stuff—like obesity, heavy drinking, and ongoing stress—can drag levels down too.
Younger guys with clear causes of low testosterone usually get treatment, while older men need a more cautious approach to see if therapy really makes sense.
Recognising the Symptoms and Impacts of Testosterone Deficiency
Low testosterone can sneak up on you, affecting everything from sex drive to muscle strength. The symptoms often creep in slowly, but if you ignore them, they can really knock down your quality of life.
Key Symptoms of Low Testosterone
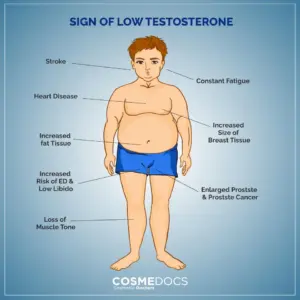
Low testosterone shows up in a bunch of ways. Fatigue that just won’t quit, shrinking muscles, and changes in body shape are big red flags.
Physical symptoms include:
- Loss of muscle mass and strength
- Extra body fat, especially around the belly
- Hair thinning on your face, body, or scalp
- Weaker bones, raising your risk for fractures
Sexual symptoms look like:
- Problems getting or keeping erections
- Fewer morning erections
- Lower sperm count and trouble with fertility
Plenty of guys notice these signs of testosterone deficiency but don’t connect them to hormones. The slow build-up can make it hard to spot what’s going on.
Muscle loss and weight gain often go hand in hand, and unfortunately, more fat can push testosterone even lower.
Effects on Sexual Function and Libido
Sexual changes are usually what send men to the doctor in the first place. When testosterone drops, libido often tanks.
Guys with low testosterone sometimes struggle with erections. They might find it tough to get or keep one long enough for sex.
Sex drive can drop off a cliff. A lot of men report less interest in sex, fantasies, or even thinking about it at all.
Performance anxiety and less satisfaction in the bedroom aren’t uncommon either. Androgen deficiency can really mess with confidence and relationships.
Fertility sometimes takes a hit, too, since sperm production drops.
Mood, Energy, and Physical Changes
Energy can fizzle out when testosterone dips. Even with plenty of sleep, you might feel wiped out.
Men with low testosterone face higher rates of depression. It’s not just in their heads—hormones really do affect mood.
Common mood changes include:
- Getting irritable or moody
- Feeling unmotivated
- Trouble focusing
- More anxiety than usual
Over time, physical changes add up. Muscles shrink, belly fat grows, and bones get weaker.
Bone loss can sneak up and lead to fractures later on. Not a fun prospect as you get older.
Sleep sometimes goes haywire, too. Falling or staying asleep can become a real challenge.
The effects of untreated testosterone deficiency can reach beyond just symptoms—overall health and even lifespan can take a hit.
Methods and Protocols for Testosterone Therapy

There’s more than one way to get testosterone into your system. Testosterone Injections, gels, patches, and pellets all have their own routines and quirks. Let’s break down the main options.
Injections and Intramuscular Administration
Most men start with intramuscular injections. Testosterone cypionate and enanthate are the usual go-tos for these shots.
Standard dosing protocols include:
- 75-100mg once a week
- 150-200mg every two weeks
- Sometimes higher doses every three or four weeks
Doctors usually inject into the glute or thigh muscle, and it’s smart to switch up the spot to avoid soreness.
Weekly shots tend to keep hormone levels more stable. Every-other-week schedules can cause peaks and valleys that don’t feel great.
During the first few months, doctors check your blood levels pretty regularly. Protocols vary in different places, but most check levels just before your next shot.
Transdermal Options: Gels and Patches
Testosterone gels offer a daily, no-needle option. You rub the gel on clean, dry skin—usually shoulders, upper arms, or belly.
Key application guidelines:
- Apply at the same time every day
- Let it dry before getting dressed
- Wash your hands after
- Hold off on swimming or showering for a while
Patches work in a similar way but don’t need to be changed as often—usually every day or two.
Some guys get skin irritation from gels or patches. Rotating where you put them can help prevent that.
Blood levels stay more stable with daily gels or patches compared to injections, which is a plus for some men.
Testosterone Pellets and Alternative Formulations
Pellets are the long-haul option. Doctors slip these tiny pellets under your skin in a quick, numbed-up procedure.
Each round of pellets lasts three to six months. You don’t have to mess with daily or weekly dosing, which is handy.
Pellet advantages include:
- No daily hassle
- Steady hormone release
- Most guys stick with this method if they try it
If you need to stop, though, the pellets have to come out with another procedure. So, they’re not as flexible as other options.
Doctors sometimes prescribe tablets or nasal gels for men who can’t use shots or skin-based treatments. These aren’t as common, but they’re out there.
Risks, Side Effects, and Considerations
Testosterone therapy isn’t risk-free. Side effects and long-term health questions mean you’ve got to go in with your eyes open. Careful monitoring and honest conversations with your doctor are a must.
Potential Side Effects of Treatment
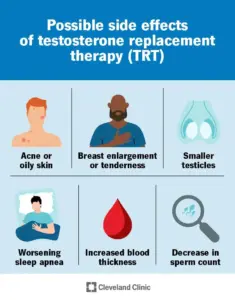
Plenty of men notice side effects when starting testosterone therapy. High red blood cell counts (erythrocytosis) can be a problem, so doctors keep tabs on that.
Common side effects include:
- Skin issues – acne, oily skin, injection site irritation
- Hormonal shifts – breast tissue growth (gynaecomastia) if testosterone turns into estrogen
- Physical changes – faster hair loss if you’re prone to male pattern baldness
- Mood changes – swings, irritability
Acne can pop up when testosterone cranks up oil production. Usually, it’s on the face, chest, or back.
Some men notice breast tissue growth if their bodies convert extra testosterone into estrogen. It’s not super common, but it happens.
If you’re genetically set up for it, testosterone can speed up male pattern baldness. That’s the tradeoff for some.
Very few men stop therapy because of skin issues, but it’s something to keep in mind before starting.
Long-term Health Risks and Monitoring
Long-term testosterone therapy needs close monitoring for serious health complications. Potential cardiovascular risks deserve attention, especially a higher risk of heart attack and stroke.
Key monitoring areas:
| Risk Area | Monitoring Required |
|---|---|
| Prostate health | PSA levels, digital examination |
| Blood parameters | Haematocrit, haemoglobin |
| Cardiovascular | Blood pressure, lipid profiles |
Prostate enlargement can become a real concern. Testosterone sometimes makes the prostate grow and may worsen existing prostate cancer.
Doctors regularly monitor prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels. If PSA rises, that might signal prostate issues worth investigating.
Cardiovascular safety means keeping an eye on heart disease risks. Blood pressure and cholesterol checks are part of the routine.
Testosterone can sometimes trigger polycythemia—basically, your body makes too many red blood cells. This thickens the blood and raises clotting risks.
Interactions with Other Medications and Conditions
Testosterone therapy interacts with a bunch of medications and health conditions. It’s important to check for these before starting treatment.
Blood-thinning medications like warfarin might need dose tweaks. Testosterone can boost anticoagulant effects, raising bleeding risk.
Diabetes meds sometimes require adjustment. Testosterone may improve insulin sensitivity, which could drop blood sugar lower than expected.
Corticosteroids with testosterone can make you retain more fluid. That combo definitely calls for extra monitoring.
Pre-existing health issues change the safety picture. Heart disease, liver problems, or sleep apnoea can all get worse with testosterone therapy.
Men with enlarged prostates face higher risks. Doctors usually reserve treatment for those with low prostate cancer risk.
Kidney disease affects how your body handles testosterone. Sometimes the dose needs adjusting to keep things safe.
Addressing Misuse and Anabolic Steroid Abuse
Testosterone misuse isn’t the same as proper, supervised therapy. Anabolic steroid abuse means much higher doses and a bigger risk of harm.
Abuse patterns include:
- Excessive dosing—using way more than therapeutic amounts
- Cycling and stacking—mixing several anabolic steroids
- Non-medical supervision—skipping proper checkups
Anabolic steroid abuse can cause harsh side effects. Liver damage, aggressive behavior, and heart problems are just a few.
Some people misuse steroids for athletic performance. It’s crucial to separate medical treatment from performance enhancement.
Psychological dependence sometimes creeps in with long-term abuse. Stopping suddenly may bring withdrawal symptoms.
Doctors provide safe dosing and regular monitoring. Balancing risks and benefits is part of good treatment.
Underground sources sell unregulated products. These can be contaminated or have unknown strengths, making them even riskier.